Key Differences between Step-Up and Step-Down Transformers
A transformer is a device that moves alternating current (AC) electricity, from one circuit to another at the same frequency usually with a voltage level adjustment. To reduce energy losses it’s more cost effective to transmit power at voltage. However for safety purposes the power should be used at voltage levels. Step up and step down transformers are used to achieve this increase in transmission voltage and decrease in utilization voltage.
The key distinction between a step up and step down transformer lies in their effect, on output voltage; a step up transformer boosts the output voltage while a step down transformer lowers it. In this article we will discusses in brief comparison of step-up and step-down transformers.
What is Step-up transformer?
A step-up transformer is a device that increases the voltage from its primary winding to the secondary winding. This type of transformer is designed to step up the voltage level, which is useful in applications such as power transmission over long distances, where high voltage reduces energy loss in transmission lines, and in various electrical devices that require higher operating voltages.
Advantages
- Increases voltage, reducing current and minimizing energy losses over long distances.
- Lower current allows for thinner, less expensive transmission wires, reducing overall costs.
- Higher voltage levels help maintain system stability and prevent voltage drops and power outages.
- Ideal for industrial applications requiring high power, such as manufacturing plants and heavy machinery.
Disadvantages
- Increased voltage demands better insulation and more robust materials to prevent electrical breakdowns and ensure safety.
- Higher voltages increase the likelihood of electrical arcing, posing safety hazards and potential equipment damage.
- Larger and more complex design leads to higher manufacturing and maintenance costs.
- Higher voltage systems require extra protection devices, such as surge protectors and circuit breakers, to handle voltage spikes.
What is Step-down transformer?
A step-down transformer is a device that decreases the voltage from its primary winding to the secondary winding. It is used to reduce the voltage level to a safer or more practical level for use in homes, offices, and various electrical appliances. Step-down transformers are commonly found in power adapters for electronic devices, household appliances, and electrical equipment where lower voltages are required for safe operation.
Advantages
- Reduces high transmission voltages to safer levels suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
- Used in a wide range of applications, from household electronics to industrial machinery.
- Generally less expensive to manufacture and maintain compared to step-up transformers due to simpler design and lower voltage ratings.
- Lower voltage levels reduce the risk of electrical shocks and make safety measures easier to implement.
Disadvantages
- Can experience energy losses, especially if not properly maintained or operated inefficiently.
- Not suitable for long-distance power transmission where higher voltage levels are necessary to minimize losses.
- While smaller than step-up transformers, they can still be bulky and heavy, posing installation challenges in confined spaces.
- Incorrect sizing can lead to inefficiencies and potential damage to the transformer and connected equipment.
Key Differences between Step-up transformer and Step-down transformer
By understanding these below differences helps in choosing the right type of transformer for specific electrical applications, depending on whether you need to increase or decrease the voltage level.</p.
Voltage Output:
- Step-up Transformer: It increases the voltage from the input to the output. This means the output voltage is higher than the input voltage.
- Step-down Transformer: It decreases the voltage from the input to the output. Therefore, the output voltage is lower than the input voltage.
Voltage Ratio:
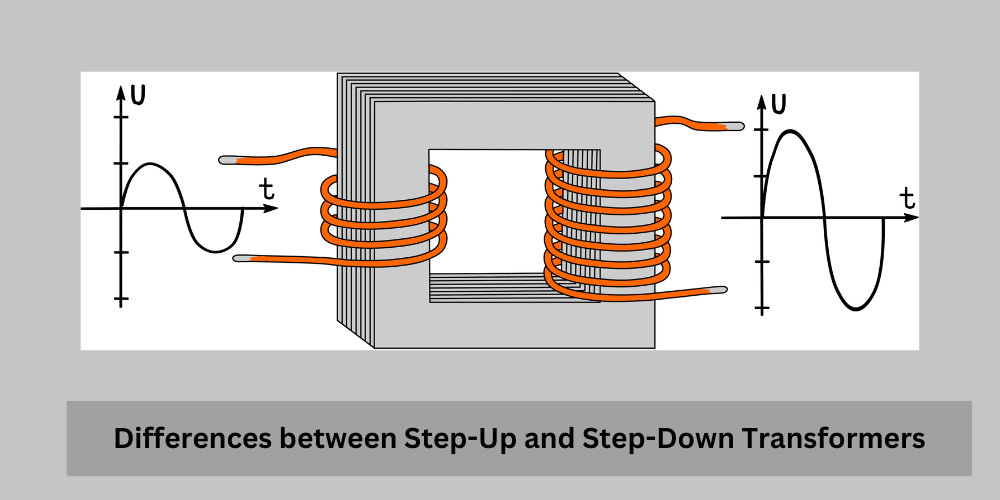
- Step-up Transformer: A step-up transformer increases the voltage from the primary winding to the secondary winding. In this case, the number of turns in the secondary winding (Ns) is greater than the number of turns in the primary winding (Np).
- Step-down Transformer: A step-down transformer decreases the voltage from the primary winding to the secondary winding. In this case, the number of turns in the secondary winding (Ns) is less than the number of turns in the primary winding (Np).
Number of Turns in Coils:
- Step-up Transformer: The secondary coil (output side) has more turns of wire than the primary coil (input side).
- Step-down Transformer: The secondary coil has fewer turns of wire compared to the primary coil.
Application
- Step-up Transformer: Used to increase voltage levels for long-distance transmission of electricity, in voltage stabilizers, and in some types of power adapters.
- Step-down Transformer: Commonly used to reduce high voltage from power lines to a safer and more usable voltage level for household appliances and electronic devices.
Transformer Design:
- Step-up Transformer: Designed to have a primary coil with fewer turns and a secondary coil with more turns.
- Step-down Transformer: Designed with a primary coil having more turns and a secondary coil with fewer turns.
Current and Power Relation:
- Step-up Transformer: While voltage increases, the current generally decreases proportionally, assuming ideal conditions (neglecting losses).
- Step-down Transformer: As voltage decreases, the current generally increases, again assuming ideal conditions.
By understanding the differences between step-up and step-down transformers, you can make an informed decision for your electrical equipment needs with Brucelectric. Whether you’re optimizing power transmission, stabilizing voltage, or powering household electronics, our experts provide tailored solutions for efficient electrical power management. Contact us today!.